Introduction to Parvati
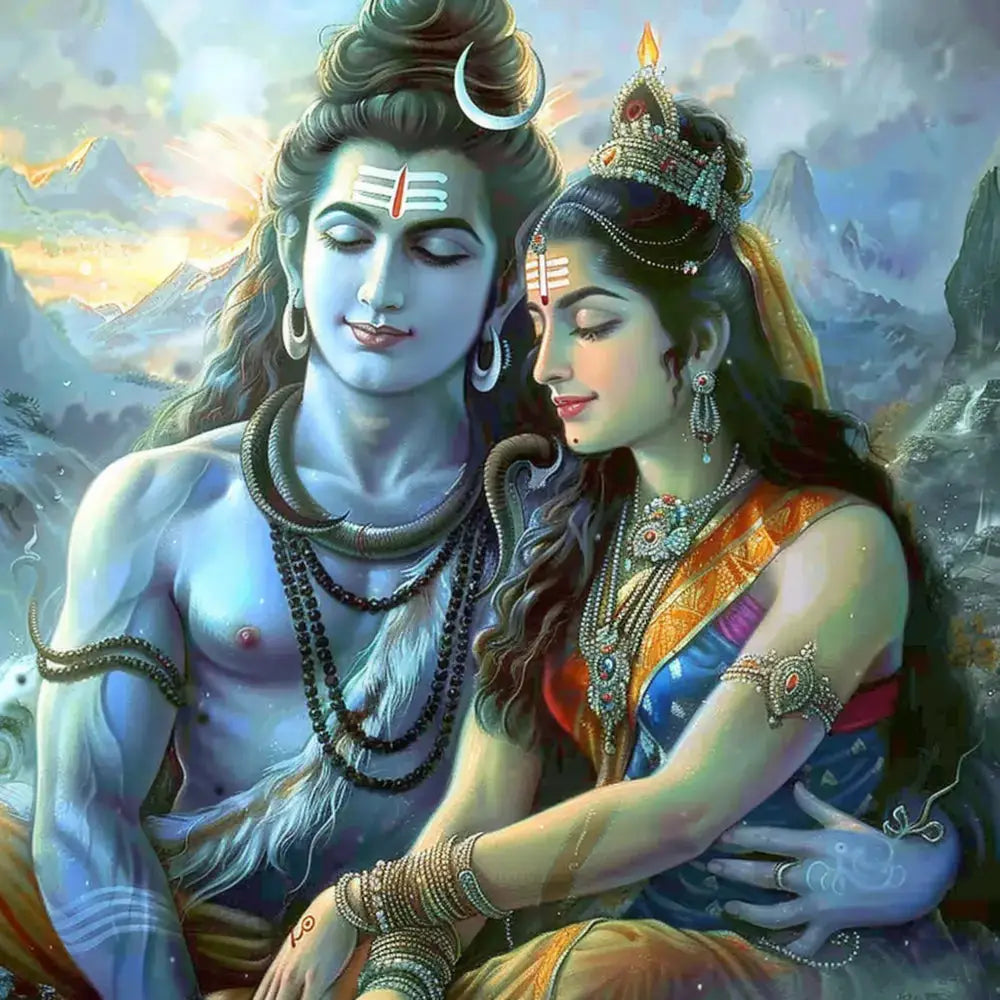
Parvati, revered as the Divine Mother in Hinduism, is a prominent deity who is intricately connected to the god Shiva. She is worshipped extensively across India and holds a significant role in various religious festivals and rituals. Her presence is often a vital part of celebrations like Diwali, Maha Shivaratri, and weddings, where she symbolizes fertility, love, and devotion.
Depiction and Attributes
- Idols and Imagery: Parvati is typically depicted with a calm and compassionate demeanor. She is often seen adorned with traditional jewelry and vibrant clothing, reflecting her connection to Indian handicrafts USA. These idols can be made from various materials and are essential pooja items.
- Sacred Symbols: She is usually associated with sacred symbols such as the diya samai (a type of lamp), incense sticks, and rangoli which are integral parts of Hindu rituals. These items can be found in many Indian homedecor online USA stores, contributing to the spiritual ambiance during festivals and daily worship.
Mythological Significance
Parvati’s narrative is deeply intertwined with themes of love and devotion. As Shiva’s consort, she plays a pivotal role in various myths and legends, embodying the ideal qualities of a devoted wife and nurturing mother. Her tales highlight attributes such as perseverance, purity, and unwavering faith.
Cultural and Religious Practices
During festivals like Diwali, it is common to offer Diwali gifts USA reflecting devotion to the Divine Mother. Items such as intricately crafted idols, sacred pooja items, and other Indian handicrafts USA are used to honor her presence. The wedding collection of traditional weddings often includes representations of Parvati and Shiva, invoking their blessings for a harmonious and prosperous married life.
Parvati’s worship is particularly accentuated during Maha Shivaratri when devotees craft elaborate offerings and rituals to celebrate the divine union of Parvati and Shiva. This festival is marked by night-long vigils, hymns, and prayers.
Parvati stands as a beacon of maternal love and moral virtue, embodied through the diverse practices and rich traditions of Hinduism. Her worship extends beyond religious boundaries, influencing cultural norms and daily life, making her a universal symbol of divine elegance and grace.
Etymology and Symbolism of Parvati
The name “Parvati” derives from the Sanskrit word “parvata,” meaning “mountain.” Parvati literally translates to “daughter of the mountain.” This is a reference to her mythological origin as the daughter of Himavan, the personification of the Himalayan mountains. In Hindu traditions, she is also known by numerous other names and epithets, each reflecting a distinct aspect of her nature and divine role.
Symbolism
- Divine Motherhood:
- Parvati is often revered as the Divine Mother, embodying the nurturing and compassionate aspects of motherhood.
- She is invoked during significant Hindu festivals like Diwali and Maha Shivaratri.
- Devotees often offer pooja items such as incense sticks, diyas, and rangolis in her honor.
- Unity and Harmony:
- Parvati represents the unity of the divine feminine (Shakti) and masculine (Shiva) energies.
- Together with Shiva, she forms the primordial cosmic couple, symbolizing balance and harmony in the universe.
- Strength and Resilience:
- In her role as Durga and Kali, Parvati symbolizes strength and the assurance of protection against evil.
- Artistic depictions of Parvati, found in Indian handicrafts in the USA, often showcase her martial aspects.
- Cultural Significance:
- Parvati plays a central role in various Hindu rituals and wedding collections, symbolizing conjugal fidelity and marital bliss.
- Her idols and images are crafted with great devotion and are available through various outlets offering Indian home decor online in the USA.
- Fertility and Prosperity:
- She is associated with fertility and prosperity, often prayed to by couples desiring offspring and householders seeking blessings.
- Devotees incorporate her symbols in wedding collections and festival decorations.
- Artistic Representation:
- Parvati is a favored subject in Indian handicrafts, with intricate statues and paintings commemorating her divine presence.
- Iconography often shows Parvati adorned with lavish jewelry, reflecting her status as a universal deity and a mother figure.
The various dimensions of Parvati’s symbolism make her one of the principal deities in Hinduism. Her imagery and artifacts are significant in the dissemination of Indian culture globally, especially to the diaspora seeking to maintain a connection to their spiritual heritage through items like idols, rangoli, and pooja essentials available online.
Mythological Origins and Lineage
Parvati, revered as the Divine Mother in Hinduism, has rich mythological origins rooted in ancient scriptures. She is commonly identified as a manifestation of Shakti, the feminine principle of divine energy, and is the consort of Lord Shiva. Parvati plays a crucial role in Hindu mythology and is deeply connected to major festivals such as Diwali and Maha Shivaratri, where offerings and pooja items like diya samai, incense sticks, and idols are significant.
Birth and Early Life
According to the Puranas, Parvati is the daughter of the mountain king Himavan and his queen, Mena. Her birth is considered divine, symbolizing purity, strength, and resilience. Raised in the majestic Himalayan environment, Parvati’s early life in mythical narratives often highlights her unmatched beauty, wisdom, and devotion to Shiva.
Reincarnation of Sati
Parvati is often identified as the reincarnation of Sati, Shiva’s first wife. Sati self-immolated after her father, Daksha, insulted her husband. Sati’s sacrifice and subsequent reincarnation as Parvati underscore themes of devotion, rebirth, and cosmic balance in Hindu traditions. This connection enriches Parvati’s significance in various religious and cultural practices, influencing offerings like beautiful rangoli patterns and traditional Indian handicrafts found in Indian home decor online in the USA.
Marriage to Shiva
In numerous tales, Parvati’s persistent meditation and austere penance eventually win Shiva’s affection. Their union represents the epitome of marital devotion and spiritual companionship. This divine pairing is celebrated in Hindu weddings and festivals, often featuring a range of associated items like wedding collections, ornamental pooja items, and intricately designed idols of the divine couple.
Divine Children
Parvati and Shiva are parents to several important deities. Their most notable sons are Ganesha, the remover of obstacles, and Kartikeya, the god of war. These divine offspring further expand Parvati’s role within the Hindu pantheon as the nurturing and protective mother, resonating deeply with family-oriented celebrations and the cultural significance of Diwali gifts in the USA.
Symbolic Representations
Parvati is depicted in various forms, emphasizing different aspects of her divinity:
- Gauri: Symbolizing purity and marital bliss.
- Durga: Representing power and the fierce aspect of motherhood.
- Kali: Portraying destruction and transformation.
These diverse forms illustrate Parvati’s expansive influence, from the gentle nurturer to the powerful protector, encompassing the entire spectrum of divine femininity in Hindu belief.
Stories and Legends of Parvati
The Origin of Parvati
Parvati, a revered Hindu goddess, has a rich mythological background. Daughter of King Himavan and Queen Mena, she is often linked with Mount Kailash. Her story begins as Sati, her previous incarnation, who self-immolated in protest of her father’s insult toward her husband, Lord Shiva. Reborn as Parvati, she undertook severe penance to marry Shiva, exemplifying devotion and determination.
Parvati and Shiva’s Marriage
The narrative of Parvati’s marriage to Shiva holds significant importance in Hindu tradition, particularly during the festival of Maha Shivaratri. Parvati’s intense austerities and devotion moved Shiva, leading to their cosmic union. Their marriage is symbolic, often celebrated in rituals and is a pivotal part of wedding collections in Hinduism. This divine couple is also depicted in various idols and indian handicrafts usa.
The Birth of Ganesha
Among the most popular legends is the creation of Ganesha, who was sculpted by Parvati from clay to guard her privacy. When Shiva unknowingly decapitated Ganesha, Parvati’s sorrow led to Shiva replacing his head with that of an elephant, giving rise to the beloved deity, Ganesha. This story is often shared during Diwali when families exchange Diwali gifts USA.
Parvati and the Banishing of Mahishasura
Parvati also manifests as Durga to combat evil. In her fierce form, she vanquishes the demon Mahishasura, symbolizing the triumph of good over evil. This epic is central to the festival of Navratri, where pooja items, incense sticks, and diya samai play vital roles in worship.
Parvati as Annapurna
In her form as Annapurna, Parvati is the goddess of nourishment. The story of Annapurna emphasizes the significance of food and compassion. Parvati’s blessings are invoked in many households, with Indian homedecor online USA often featuring her imagery to symbolize abundance.
Symbolism in Daily Life
Parvati embodies the essence of devotion, fertility, and power. Her stories inspire many intricate rangoli designs during festivities and are intrinsic to the crafting of Indian handicrafts USA. The goddess’s influence extends to various cultural artifacts and rituals, shaping the spiritual fabric of Hindu households.
Parvati’s legends underscore her roles from a nurturing mother to a fierce protector, demonstrating the multifaceted nature of the Divine Mother in Hinduism.
Parvati’s Role in the Hindu Trinity
Parvati, an epitome of divine motherhood, holds a significant place in the Hindu trinity known as the Tridevi. Comprising Parvati, Lakshmi, and Saraswati, the Tridevi represents the feminine aspect of the divine and complements the Trimurti—Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva. Within this sacred trio, Parvati is often associated with the potent, nurturing, and occasionally wrathful aspects of womanhood.
As a Compassionate Mother
Parvati is often venerated as the compassionate mother within Hinduism. She symbolizes fertility, love, and devotion, which makes her an ideal figure for various familial and maternal aspects. Her depiction with her children, Ganesha and Kartikeya, exemplifies her role as a devoted and loving mother.
The Consort of Shiva
As the consort of Shiva, Parvati embodies the perfect balance to his ascetic lifestyle. While Shiva represents destruction and transformation, Parvati provides the nurturing energy required for creation and preservation. Together, they signify the harmonious balance between asceticism and domestic life.
Divine Feminine Power
Parvati is also considered a manifestation of Shakti, the divine feminine power. In this role, she assumes multiple forms, from the benevolent goddess Annapurna, who provides food and nourishment, to the fierce warrior goddess Durga, who combats evil forces. During festivals like Diwali, her idols can be found alongside diya samai and incense sticks, symbolizing her presence in homes across the world, including USA households where Indian home decor options are popular.
Role in Rituals and Ceremonies
In Hindu rituals and ceremonies, Parvati’s influence is pervasive. From the timeless tradition of creating rangoli designs during festivals to the elaboration of pooja items, her essence is omnipresent. For events such as maha shivaratri, Parvati is worshipped fervently alongside Shiva, with devotees seeking blessings for marital harmony and prosperity.
Representation in Indian Art
Parvati’s significance extends to Indian art and handicrafts as well. Her statues, idols, and intricate designs are prevalent in Indian handicrafts available in the USA. These expressive artifacts are often part of the wedding collection, making them cherished keepsakes. They also feature prominently in Diwali gifts and Indian home decor online marketplaces in the USA.
Symbol of Women’s Strength
In her many forms, including that of Kali and Durga, Parvati symbolizes the various facets of womanhood, from nurturing and tenderness to strength and ferocity. This multifaceted nature makes her an enduring figure of inspiration and reverence among devotees.
Understanding Parvati’s role within the Hindu trinity offers deeper insight into her profound impact on Hindu spirituality and daily life.
Manifestations and Avatars of Parvati
Hindu mythology recognizes Parvati, the Divine Mother, in numerous manifestations and avatars, each representing different aspects of her divine nature. Her avatars are widely celebrated in festivals such as Navratri, Maha Shivaratri, and Diwali. Moreover, devotees seek her blessings using various pooja items, idols, incense sticks, and diya samai. Here is an overview of some prominent manifestations of Parvati:
Navadurga
Navadurga represents nine different forms of Parvati, each worshipped during the nine days of Navratri:
- Shailaputri: Symbolizing the daughter of the mountains.
- Brahmacharini: Embodying austerity and penance.
- Chandraghanta: Known for her great warrior prowess.
- Kushmanda: The creator of the universe.
- Skandamata: Represents the mother of Skanda or Kartikeya.
- Katyayani: The powerful warrior goddess.
- Kalaratri: The fearsome form, depicted fighting demons.
- Mahagauri: Symbolizes purity and compassion.
- Siddhidatri: The goddess who provides supernatural powers.
Mahavidyas
Parvati manifests as the Mahavidyas to demonstrate the supreme knowledge and power. These ten goddesses include:
- Kali: The destroyer of evil and the remover of darkness.
- Tara: The goddess of compassion and the protector.
- Tripura Sundari: The epitome of beauty and love.
- Bhuvaneshvari: The sovereign queen of the universe.
- Chinnamasta: Signifying self-sacrifice and vivid energy.
- Bhairavi: The fierce and vibrant form.
- Dhumavati: The goddess of poverty and suffering.
- Bagalamukhi: The paralyzer of enemies.
- Matangi: Representing control and domination.
- Kamala: The goddess of prosperity and wealth.
Other Significant Avatars
- Durga: Known for slaying the buffalo demon Mahishasura, Durga represents the ultimate protective mother.
- Annapurna: The provider of food and nourishment.
- Lalita: The blissful and joyous goddess.
Festival Celebrations
During festivals like Diwali, homes are adorned with Indian home decor online USA, ranging from rangoli designs to intricate handicrafts. Traditional practices include the exchange of Diwali gifts USA, emphasizing the divine presence of Parvati. Her idols, surrounded by incense sticks and pooja items, are also central to worship, enhancing spiritual ambiance.
Understanding the divine aspects of Parvati facilitates a deeper reverence for her presence in Hinduism. From her nurturing forms to her fierce protectiveness, the Divine Mother serves as an ultimate beacon of love, strength, and compassion.
Parvati’s Relationship with Shiva
Parvati, the revered Divine Mother in Hinduism, shares a profound relationship with her consort, Shiva, known as the Destroyer in the Holy Trinity of Hindu gods. Their union symbolizes the harmonious balance of energy in the cosmos. The narrative of their relationship is filled with numerous rich and meaningful aspects that illuminate their divine partnership.
Shiva and Parvati’s bond represents the quintessential union of Shakti (power) and Shiva (consciousness). This divine pairing is often depicted in forms of idol worship and is celebrated extensively during festivals like Maha Shivaratri. Pooja items such as incense sticks, diya samai, rangoli, and various items from Indian homedecor online in USA enhance the celebratory fervor of these festivals.
First Meeting Parvati’s first meeting with Shiva is shrouded in myth and mystery. According to legend, Parvati, the daughter of the mountain king Himavan, performed severe penance to win Shiva’s love, who was deep in meditation. Her dedication and austerities reflected her profound adoration and relentless commitment, eventually winning Shiva’s heart.
Marriage Their wedding is one of the most celebrated events in the Hindu tradition. It is a source of inspiration for many wedding collections. The grandeur of their divine wedding is often depicted in Indian handicrafts available in the USA. This sacred union emphasizes the importance of marital bonds and the spiritual synchronization of male and female energies.
Mutual Devotion Both deities are portrayed as embodying an immense degree of mutual respect and devotion. Parvati is often seen revered in various forms of idols that depict her in deep meditation alongside Shiva. This relationship dynamic highlights the significance of companionship and mutual support in achieving spiritual enlightenment.
Role in Family Parvati and Shiva’s relationship also shines through their family life. They are the parents of two significant Hindu gods, Ganesha and Kartikeya. Their divine family is often the centerpiece of Diwali gifts in the USA, symbolizing familial unity, prosperity, and protective energies.
Through their iconography, rituals, and stories, the divine relationship between Parvati and Shiva establishes a framework of ideal partnership dynamics in various facets of life, from spiritual pursuits to family relationships. Their divine union is a central narrative in the tradition, revered and celebrated with a plethora of pooja items and Indian homedecor online, especially during auspicious occasions.
Temples and Worship Practices
Parvati, revered as the Divine Mother in Hinduism, is worshipped in many temples across India and beyond. These temples often house intricately designed idols of Parvati, which are central to the spiritual ambiance. Some well-known temples dedicated to Parvati include:
- Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai
- Kamakhya Temple in Assam
- Attukal Bhagavathy Temple in Kerala
- Dakshineswar Kali Temple in Kolkata
Worship practices of Parvati involve rituals deeply rooted in tradition. Devotees often use pooja items such as incense sticks, diya samai, and vibrant rangoli designs. Worshippers light diya samai to signify the removal of darkness and the spread of divine light.
Maha Shivaratri, a major festival dedicated to Parvati and her consort Shiva, sees devotees engaging in intense prayers, fasting, and night-long vigils. Temples are decorated with indian homedecor online usa like indian handicrafts usa, significantly enhancing the festive atmosphere.
During festivals like Diwali, worshippers across the world, including those sourcing diwali gifts usa, offer special prayers to Parvati for prosperity and well-being. They adorn their homes with pooja items and create intricate rangoli patterns, symbolizing welcome and happiness.
Wedding collections within temples often feature elaborate ceremonies and blessings sought from Parvati, who is seen as a symbol of marital bliss and loyalty. Special pooja items and idols of Parvati and Shiva are used during these ceremonies to invoke divine blessings.
Parvati’s worship in households mirrors temple practices. Idols of Parvati, often acquired from indian handicrafts usa, grace home altars. Devotees recite hymns and perform rituals with incense sticks, flowers, and other pooja items to seek her blessings for harmony and protection.
Thus, temples and worship practices dedicated to Parvati are integral to celebrating her divine presence, fostering a deep spiritual connection among her devotees.
Parvati in Art, Literature, and Popular Culture
Parvati, revered as the divine mother in Hinduism, has profoundly influenced art, literature, and popular culture. Her representations span across various mediums, each reflecting unique aspects of her divinity and significance.
Art
- Sculpture: Parvati is depicted in various forms, from serene and benevolent to powerful and fierce. Temples across India feature sculptures of Parvati, often accompanied by Shiva. These works of art are not only religious symbols but also masterpieces of Indian handicrafts. Sculptures available in the Indian handicrafts USA market capture her divine essence, offering presence in homes and temples abroad.
- Paintings: Traditional Indian paintings, such as Madhubani and Tanjore, often portray Parvati. Her depiction in these art forms ranges from the loving, nurturing mother to the regal goddess. Such artworks, available through indian homedecor online USA, make for exquisite Diwali gifts USA, infusing homes with divine grace and beauty.
Literature
- Epics and Puranas: Parvati features prominently in Hindu texts like the Puranas and the Mahabharata. She is portrayed as a devoted wife to Shiva and a loving mother to Ganesha and Kartikeya. Her stories often emphasize devotion, sacrifice, and the balance of power within the feminine divine.
- Poetry and Folk Tales: Regional folklore and poetry celebrate Parvati’s virtues and adventures. Her tales during Maha Shivaratri highlight her meditation and devotion, inspiring countless versions in different Indian languages, thus enriching the vast domain of Indian mythology.
Popular Culture
- Movies and Television: Modern interpretations of Parvati are seen in numerous Indian films and television series. These portray her mythical narratives, often during significant festivals like Diwali or Navaratri, emphasizing her roles within the divine family and her influence on human virtues.
- Fashion and Jewelry: Parvati’s imagery inspires bridal wear and the wedding collection in modern fashion. Traditional bridal ornaments echo the divine adornments of the goddess, making them staples in Indian and global wedding cultures.
- Home Decor and Rituals: Idols of Parvati, along with pooja items like incense sticks, rangoli designs, and diya samai, embody her presence in daily rituals. The online availability of these items ensures that devotees in the USA can maintain cultural practices and celebrate festivals with authenticity and devotion.
Through diverse expressions in art, literature, and popular culture, Parvati continues to inspire, embodying the multifaceted nature of the divine feminine and its integral role in Hindu spirituality and life.
Parvati’s Influence on Modern Hindu Practices
Parvati, the Divine Mother in Hinduism, holds significant influence over various contemporary Hindu practices. Her presence is deeply embedded in numerous rituals, festivals, and daily religious activities that are observed by millions of devotees.
Festivals and Celebrations
- Diwali: During the festival of Diwali, offerings to Parvati include traditional items such as incense sticks, diya samai, and rangoli. Families in the USA often purchase Indian home decor online and Diwali gifts to honor her presence in their homes.
- Maha Shivaratri: This festival, dedicated to Lord Shiva, also celebrates Parvati as his consort. Devotees observe fasting, night vigils, and offer pooja items including flowers, milk, and incense sticks to her.
- Karva Chauth: Married women fast from sunrise to moonrise for the well-being of their husbands, invoking Parvati’s blessings as the epitome of marital devotion.
Icons and Idols
- Idols: Parvati’s idols are commonly found in households, temples, and during festival decorations. These idols are often sourced from skilled artisans and Indian handicrafts stores, including those available in the USA.
- Home Decor: Items depicting Parvati, such as murals and statues, play a significant role in Indian home decor online, symbolizing protection and prosperity.
Rituals and Daily Practices
- Worship: Parvati is worshipped daily through items such as incense sticks, floral offerings, and chanting of mantras.
- Marriage Ceremonies: In joyful wedding celebrations, invoking Parvati’s blessings is integral. Wedding collections often include elements that symbolize Parvati’s marital fidelity and blessings for a prosperous married life.
Material Culture
- Craftsmanship: Fine craftsmanship of Parvati’s idols and decor items signifies not just religion but cultural heritage, with high demand in the Indian handicrafts USA market.
- Pooja Enhancements: The use of intricately designed pooja items reflects Parvati’s artistic influence, showcasing traditional skills adapted for modern aesthetics.
Empowerment and Devotion
- Women’s Empowerment: Parvati stands as a powerful figure of strength and devotion, inspiring modern women. Her stories and statues in homes act as a beacon for resilience and love.
- Educational Narratives: Stories of Parvati are incorporated into educational curriculums, religious discourses, and literature, promoting cultural and spiritual knowledge across generations.
Through these elements, Parvati continues to impact and inspire modern Hindu practices, especially for Indian communities globally, including those who access cultural treasures online from the USA.
Conclusion: Parvati’s Enduring Significance
Parvati holds a prominent and enduring place in Hindu mythology and religious practice. As the Divine Mother, she embodies virtues such as compassion, devotion, and strength, making her a central figure in the spiritual lives of millions. Her multifaceted roles as consort of Shiva and mother to deities like Ganesha and Kartikeya enrich her narrative and elevate her status among devotees.
Cultural Influence and Devotional Practices
Parvati’s significance transcends her mythological tales, manifesting in various cultural celebrations and rituals. During Maha Shivaratri, Parvati is venerated alongside Shiva through elaborate poojas, where devotees use various pooja items, including incense sticks, idols, and diya samai. Her influence extends to household decorations, with Indian home décor online USA offering a plethora of decorative elements like rangoli and Indian handicrafts USA.
Symbol of Matrimony and Motherhood
Her role as a symbol of perfect matrimony and motherhood continues to inspire many, with her depiction frequently found in the wedding collection of Hindu ceremonies. Parvati’s story provides a blueprint for marital harmony, and her blessings are sought by couples for a prosperous and harmonious relationship.
Devotion Through Festivities
Parvati’s significance is further highlighted during festivals. In particular, Diwali celebrations often include offerings and Diwali gifts USA dedicated to her, symbolizing the nurturing aspect of prosperity and familial bonds.
Artistic Representation
Parvati’s representation in art is prevalent, ranging from intricate idols to various forms of Indian handicrafts USA. These artistic expressions are not only objects of worship but also serve as important cultural artifacts, preserving her story for future generations.
Commercial and Spiritual Integration
Contemporary platforms selling Indian home décor online USA and pooja items contribute to spreading her influence, making it easier for devotees worldwide to honor her through rituals and decorations. The availability of Indian handicrafts USA and specialized items for Maha Shivaratri and weddings further integrate her presence into daily lives, both spiritually and commercially.
Conclusion: Parvati’s Enduring Significance
Thus, Parvati remains a timeless figure whose attributes and stories continue to inspire devotion and reverence. Her impact is profoundly visible not only in religious ceremonies but also in the art, culture, and daily lives of those who revere her, confirming her enduring significance in Hinduism.